Aluminum Blister Packaging
Aluminum blister packaging is a widely used sealed packaging technology in the fields of pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. Its core feature is the use of aluminum foil material to achieve high barrier properties and protection.
Aluminum blister packaging is a safe multi-layer packaging solution designed to protect unit-dose products, especially pharmaceuticals. It consists of a formed cavity (blister) and a lidding material, with aluminum typically used as the sealing layer. This type of packaging is known for its excellent barrier properties, tamper-evident performance, and user convenience.
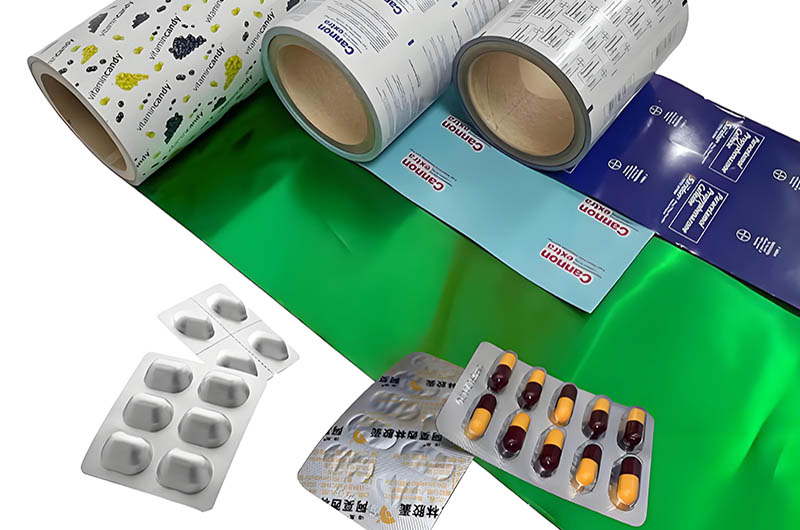
Aluminum blister packaging, as a high-performance and multifunctional packaging solution, has broad application prospects in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, and electronics.
Product Advantages
- Excellent barrier performance: Aluminum blister packaging can effectively block oxygen, moisture, light, and odors, ensuring product quality stability.
- Good mechanical properties: It has high strength and toughness, capable of withstanding certain pressure and impact to protect the contents from damage.
- Flexible processing performance: It can be processed into various shapes and sizes of blisters through thermoforming, cold forming, and other processes.
- Exquisite printing effect: The surface of the aluminum foil can be printed and decorated with high quality to enhance product appeal.
- Diversified opening methods: Supports various opening methods such as push-through, peelable, and peel-push types to meet the needs of different products.
Aluminum blister packaging, especially cold-formed aluminum blister packaging, is a specialized pharmaceutical packaging solution designed to provide maximum protection for sensitive medications. This packaging method uses double-sided aluminum foil to completely block environmental factors such as moisture, oxygen, and light.
Aluminum blister packaging balances protection, compliance, and usability. Its versatility spans various industries and continues to make progress in sustainability and integration of smart technologies. Whether using thermoforming or cold-forming designs, aluminum consistently plays a key role in ensuring product safety and longevity.
Structural Classification and Material Composition of Aluminum Blister Packaging
Aluminum / Aluminum (ALU/ALU) Blister Structure
Aluminum / aluminum blister packaging, also known as cold-forming solid pharmaceutical composite hard film or cold aluminum, is currently one of the blister packaging forms with the best barrier performance. Its basic structure usually consists of the following three layers:
- Outer protective layer (OPA): Usually made of polyamide (nylon) material, with excellent ductility and mechanical strength, providing necessary stretch performance during cold forming.
- Middle aluminum foil layer (AL): Serving as the core barrier layer, using aluminum foil with a purity of over 99.5%, with a typical thickness of 45–60μm. The aluminum foil is completely opaque and has an extremely low water vapor transmission rate and excellent gas barrier properties.
- Inner heat-seal layer (PVC): Usually made of polyvinyl chloride material, providing good heat-sealing performance to ensure a reliable seal between the blister and PTP aluminum foil.
With technological development, various modified ALU/ALU structures have also emerged, such as PA/AL/PA/PVC, PVC/PA/AL/PA/PVC, PA/AL/PE, PA/AL/CPP, PE/PA/AL/PA/PE, etc. These structures mainly adjust the material combinations and layers to meet specific packaging requirements of different products, such as halogen-free environmental protection requirements.
Aluminum / Plastic (ALU/plastic) Blister Structure
Aluminum / plastic blister packaging is the most common form of blister packaging and mainly consists of the following parts:
Aluminum foil layer (AL): Serves as the main barrier layer, with a typical thickness of 20–30μm. It offers excellent moisture-proof, oxygen-barrier, and light-blocking properties.
Plastic rigid film layer: Common plastic materials include:
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): Has good transparency and formability, making it one of the most widely used blister materials.
- Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC): Has extremely high barrier properties and is often laminated with PVC to enhance the overall barrier effect.
- Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE): Possesses extremely excellent moisture barrier performance, far superior to materials such as PVC and PP.
- Polypropylene (PP) and Polyester (PET): Have high heat resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for special application scenarios.
Typical structures of aluminum / plastic blisters include PVC/PE/PVDC, PVC/PE/PVDC/PVC composite rigid films. These structures achieve sufficient barrier protection while maintaining good forming properties through combinations of different materials.
Aluminum and Paper / PET Composite Blister Film Structure
Aluminum and paper / PET composite blister films are mainly used in applications requiring high barrier performance and peelability:
- Aluminum foil layer (AL): Serves as the core barrier, typically with a thickness of 20–30μm.
- Paper layer: Provides a certain level of mechanical strength and peelability, and adds eco-friendly attributes to the packaging.
- Polyester film (PET): Commonly laminated with aluminum foil to enhance overall mechanical and heat-sealing performance.
Typical forms of such composite structures include Paper/AL/HSL, PET/AL/HSL, Paper/PET/AL/HSL. HSL refers to the heat-seal layer, usually made of specially formulated hot melt adhesives or polymer materials to ensure good heat-sealing performance.
Comparative Analysis of Material Properties
| Material Type | Main Advantages | Main Disadvantages | Typical Thickness Range | Barrier Performance |
| Aluminum Foil (AL) | Completely opaque, extremely low permeability, excellent moisture resistance, high strength | Relatively high cost, opaque, difficult to process | 20–60μm | Very High |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | High transparency, good formability, moderate cost | Moderate barrier property, limited heat resistance | 150–300μm | Medium |
| Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) | Extremely high barrier, good chemical resistance | High cost, difficult to process | 15–30μm | Very High |
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE) | Superior moisture resistance, high temperature resistance, excellent chemical stability | Extremely high cost, limited supply | 15–152μm | Very High |
| Polypropylene (PP) | High temperature resistance, high mechanical strength, good chemical resistance | Moderate transparency, poor heat sealability | 150–300μm | Medium |
| Polyester (PET) | High strength, high temperature resistance, good transparency | Relatively high cost, moderate barrier properties | 12–50μm | Medium |
| Polyamide (OPA) | High mechanical strength, good flexibility, excellent puncture resistance | Moderate barrier property, relatively high cost | 15–30μm | Medium |
| Paper | Environmentally friendly, low cost, good printability | Poor barrier property, moisture-sensitive, low strength | 50–200μm | Very Low |
Aluminum Foil Thickness and Tolerance Standards
Aluminum Foil Thickness and Tolerance in ALU/ALU Blister Packs
In ALU/ALU blister structures, aluminum foil is the most critical component. Its thickness directly affects the barrier performance and mechanical strength of the packaging. According to industry standards and actual application data, the thickness of aluminum foil in ALU/ALU blisters usually falls within the following range:
Standard thickness: 45–60μm Tolerance range: ±0.003mm (i.e., ±3μm)
This tolerance requirement is very strict, primarily to ensure consistency and reliability during subsequent processing of the foil. Uneven thickness may lead to difficulties in achieving the standard adhesive coating amount during the coating process, which in turn affects the heat-seal strength between the aluminum foil and the PVC rigid film. Additionally, uneven thickness may cause foil breakage during processing, reducing production efficiency.
Aluminum Foil Thickness and Tolerance in ALU/Plastic Blister Packs
In ALU/plastic blister structures, the aluminum foil is generally thinner than that in ALU/ALU structures, with the following characteristics:
- Standard thickness: 20–30μm
- Tolerance range: ±0.002mm (i.e., ±2μm)
This tolerance requirement is even stricter than that of ALU/ALU structures, mainly because in ALU/plastic structures, aluminum foil is typically used as a lidding material and must be heat-sealed with the plastic rigid film. Stricter tolerance control helps ensure the consistency and reliability of heat-sealing strength.
Aluminum Foil Thickness and Tolerance in Aluminum/Paper or PET Composite Blisters
In aluminum/paper or aluminum/PET composite blister structures, the aluminum foil thickness is usually similar to that in ALU/plastic structures, but the tolerance requirements may differ slightly:
- Standard thickness: 20–30μm
- Tolerance range: ±0.003mm (i.e., ±3μm)
This tolerance range aligns with the national standard for pharmaceutical aluminum foil, primarily because this type of composite structure is also widely used in pharmaceutical packaging. As the primary barrier layer, the uniformity of the aluminum foil thickness directly impacts the protective performance of the packaging.
Effects of Different Alloy Materials on Aluminum Foil Performance
The aluminum foil used in blister packaging typically adopts specific aluminum alloy materials to meet various performance requirements. Below are several commonly used aluminum alloy materials and their characteristics:
| Alloy Type | Main Characteristics | Typical Applications | Advantages |
| 8011, 8011A Series | Contains iron and silicon; moderate strength and good surface quality | Pharmaceutical blister packaging, food packaging | Good comprehensive performance, high cost-effectiveness |
| 8021, 8079 Series | Special formulation, high purity, very low impurity content | High-end pharmaceutical packaging, sensitive product packaging | High purity, stable performance |
Functions and Pros & Cons Analysis of Various Blister Types
Functions and Pros & Cons of ALU/ALU Blisters
Main Functions:
ALU/ALU blisters are mainly used for packaging products that require extremely high barrier performance, especially those sensitive to oxygen, moisture, and light.
Main functions include:
- Provide complete barrier protection: Almost completely blocks water vapor, oxygen, and UV light to ensure product quality stability.
- Individual unit protection: Each blister forms an independent, completely sealed unit. Removing some of the contents does not affect the sealing of the remaining medicines.
- Good mechanical protection: Offers high compressive strength and puncture resistance to protect contents from physical damage.
- Excellent temperature resistance: Can withstand significant temperature variations, suitable for various storage and transportation environments.
Advantages:
- Extremely high barrier performance: Currently the best barrier blister packaging, almost completely blocks gas, moisture, and light.
- Extended product shelf life: Effectively prevents oxidation, moisture, and spoilage, significantly extending product shelf life.
- Suitable for harsh environments: Especially ideal for high temperature and high humidity environments such as tropical regions.
- Excellent printability: The aluminum foil surface allows high-quality printing to enhance visual appeal.
- High safety: Each blister is independently sealed, reducing contamination risks and improving product safety.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost: Compared to aluminum-plastic blisters, ALU/ALU blisters have higher material and processing costs.
- Heavier weight: Greater use of aluminum foil increases overall packaging weight and shipping costs.
- Requires specialized equipment: Cold-forming requires dedicated cold-forming machines, increasing investment in equipment.
- Difficult to open: Compared to aluminum-plastic blisters, ALU/ALU blisters are harder to open, which may affect user experience.
- Difficult to recycle: Aluminum-plastic composite structures are difficult to recycle, increasing environmental pressure.
Functions and Pros & Cons of ALU/Plastic Blisters
ALU/plastic blisters are the most common form of blister packaging, mainly used in the following scenarios:
- Basic barrier protection: Offers good moisture, oxygen, and light protection to shield contents from external factors.
- Product display: Transparent or semi-transparent plastic film makes the contents clearly visible, aiding product presentation and identification.
- Ease of access: Easy to open by pressing the blister, allowing convenient product use.
- Cost control: Provides good protective performance while keeping packaging costs within a reasonable range.
Advantages:
- High cost-effectiveness: Compared to ALU/ALU blisters, lower material and processing costs with higher overall value.
- Lightweight: Lower total weight reduces shipping costs and energy consumption.
- Good transparency: Plastic films typically have high transparency, making product display easier.
- Easy to form: Mature thermoforming process with relatively low equipment investment, suitable for mass production.
- Easy to open: Users can open the blister easily with a simple press, improving user experience.
Disadvantages:
- Limited barrier performance: Compared to ALU/ALU blisters, offers less protection, especially against oxygen and moisture.
- Unsuitable for sensitive products: Insufficient protection for products highly sensitive to oxygen and moisture.
- Limited heat resistance: Plastic films have limited heat tolerance and are not suitable for high-temperature environments or sterilization.
- Sealing challenges: Heat-seal quality is affected by multiple factors, potentially leading to sealing defects.
- Environmental concerns: Environmental issues with plastic materials are increasing, facing regulations such as plastic bans.
Functions and Pros & Cons of Aluminum/Paper or PET Composite Blisters
Aluminum/paper or aluminum/PET composite blisters are mainly used in the following scenarios:
- Balanced barrier and easy opening: Provides good barrier performance while enabling easy-to-open features.
- Anti-counterfeiting and traceability: Complex composite structures increase the difficulty of counterfeiting and support product traceability and authentication.
- Environmental and sustainability: Combining paper materials improves environmental performance and recyclability.
- Special opening methods: Supports peelable, push-through-peel, and other opening designs to meet diverse product needs.
Advantages:
- Flexible opening methods: supports various opening styles such as push-through, peelable, and peel-push combination.
- Excellent printing performance: paper or PET surfaces allow high-quality printing and decoration, enhancing product appeal.
- Improved environmental performance: combining with paper materials reduces plastic usage and enhances packaging sustainability.
- Anti-counterfeiting function: the complex composite structure increases counterfeiting difficulty, enhancing product security.
- Lightweight design: compared to pure aluminum structures, it's lighter in weight, reducing transportation costs.
Disadvantages:
- Limited barrier performance: compared with pure aluminum structures, composite structures have reduced barrier effectiveness.
- High processing complexity: multilayer composite structures increase processing difficulty and quality control challenges.
- Higher cost: the complex structure and special processing technologies increase material and production costs.
- Mechanical strength challenges: multilayer composites may lead to reduced overall mechanical strength, affecting protective performance.
- Difficult recycling: the mixture of different materials complicates recycling, resulting in higher environmental treatment costs.
Comprehensive Comparison of Three Types of Blister Packaging
| Performance Indicator | ALU/ALU Blister | ALU/plastic Blister | Aluminum-paper/PET Composite Blister |
| Cost | High | Low | Medium to High |
| Weight | Heavy | Light | Medium |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent / Semi-transparent | Partially Transparent |
| Opening Convenience | Difficult | Easy | Moderate |
| Processing Difficulty | High | Low | Medium to High |
| Environmental Performance | Moderate | Low | High |
| Applicable Temperature Range | Wide | Limited | Moderate |
| Printability | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Sealing Reliability | High | Moderate | High |
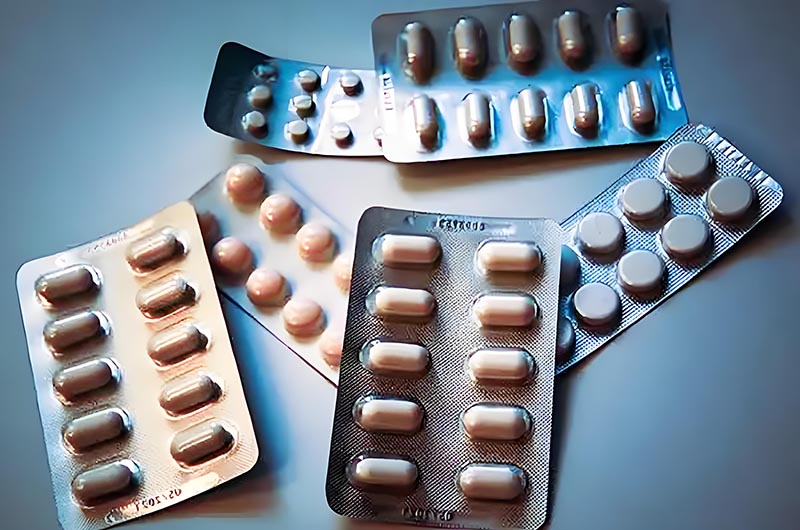
Aluminum Blister Packaging Standard Size
| Aluminum Foil Thickness (mm) | 0.025 – 0.028 | 0.02 – 0.023 |
| Tolerance (mm) | +/- 8% of AL foil | |
| Density (GSM/CC) | 2.71 | 2.71 |
| Aluminum Foil Weight (GSM) | 68 | 54 – 67 |
| Aluminum Foil Surface | Matte / Bright | |
| Temper | Hard Temper | |
| Primer (GSM) Max | 1 – 1.5 | |
| Heat Seal Lacquer | 3-5 GSM (Standard) | |
| 6-8 GSM (Special) | ||
Classification of Aluminum Blister Packaging
Blister packaging can be classified based on barrier properties, forming methods, opening methods, and light barrier performance. When designing a pharmaceutical blister packaging system, it is essential to choose the appropriate blister packaging based on the characteristics of the medication.
Classification of Blister Aluminum Packaging by Forming Method
| Forming Method | Material Classification |
| Thermoforming | PVC, PP, PE, PET, COC, PVC/PE, PVC/PVDC, PVC/PVDC/PVC, PVC/PCTFE/PVC, PVCPVDC/PVC, PVC/PCTFE/PVC |
| Cold Stamping | AL/PE, PA/AL/PVC, PA/AL/PE |
| Thermoforming and Cold Stamping | PVC + PA/AL/HSL |
Thermoformed aluminum blister packaging involves heating plastic materials to soften them, followed by shaping them in a mold under pressure.
Cold-stamped aluminum blisters are formed by applying pressure to the material using a stamping die at room temperature.
Classification of Blister Aluminum Packaging by Opening Method and Common Material Structures
Blister packaging typically employs the following four structural methods: push-through, peel-off, peel-and-push, and tear-open.
| Opening Method | Common Material Structures |
| Direct Push-Break | OP/AL/HSL, OP/AL/PVC |
| Peel-Off | Paper/AL/HSL, PET/AL/HSL, Paper/PET/AL/HSL |
| Peel-and-Push | Paper/AL/HSL, PET/AL/HSL, Paper/PET/AL/HSL |
| Packaging Type | Description | Material Composition | Features and Applications |
| Push-Through Blister Packaging | Push-Through Blister Packaging is designed to dispense medication doses by pushing them through the lidding. Typically, hard temper aluminum is used because it has sufficient strength to maintain its integrity without deformation or rupture when the medication is pushed through. Although soft temper aluminum is sometimes used, it is less common due to its lower puncture strength. To enhance child resistance, lidding with higher puncture strength is sometimes chosen. | Hard temper aluminum (commonly used) Soft temper aluminum (less common) | Suitable for packaging that requires high strength and durability. Hard temper aluminum effectively prevents leakage and ensures safety, and is designed to prevent children from opening the packaging. |
| Peel-Open Blister Packaging | Peel-Open Blister Packaging is designed to dispense medication doses by peeling the lidding away from the tray. The lidding typically consists of aluminum combined with paper backing or paper/PET backing. The paper backing adds additional strength and support, while the aluminum provides a protective barrier to prevent environmental factors from affecting the medication. | Aluminum + Paper backing or paper/PET backing | Suitable for packaging designs that are easy for users to open, while effectively protecting the medication from environmental factors. Widely used for pharmaceutical and health product packaging. |
| Peel-Push Blister Packaging | Peel-Push Blister Packaging combines both peeling and pushing actions. The user first peels back one layer of the lidding and then pushes the medication dose through the remaining aluminum foil. The lidding is typically made of a multi-layer material consisting of paper/PET/aluminum foil/HSC. The paper and PET layers provide support and strength, while the aluminum foil ensures protection against moisture, light, and other environmental factors, and the HSC layer strengthens the overall structural integrity. | Paper/PET/Aluminum foil/HSC (high-strength cardboard or similar material) | Suitable for packaging that requires multiple protective layers, effectively preventing moisture or contamination, while being easy to open. Ideal for packaging that requires both peeling and pushing actions. |
| Tear-Open Packaging | Tear-Open Packaging is designed to dispense medication doses by tearing open the package. The materials used typically include a combination of paper/PET/aluminum foil/HSC. The paper layer provides the strength needed for tearing, while the PET and aluminum foil layers offer excellent protective barriers to keep the medication safe from environmental factors. The HSC layer adds durability and support, ensuring that the package remains intact during handling and shipping. | Paper/PET/Aluminum foil/HSC (high-strength cardboard or similar material) | Suitable for simple and easy-to-open packaging designs, allowing for easy tearing while effectively protecting the medication from external factors. Commonly used for pharmaceutical, nutritional products, and other items that need protection from environmental influences. |
Classification of Blister Aluminum Packaging by Light Barrier Performance and Common Material Structures
| Light Barrier Property | Common Material Structures |
| Transparent | PVC, PP, PET, PE, PVC/PE, PVC/PVDC, PVC/PE/PVDC, PVTFE/PVC, PVC/PVDC/PVC |
| Translucent | Colored-PVC, PP, PET, PE |
| Opaque | AL/PE, PA/AL, PVC, PVC + PA/AL/HSL |
Thickness of Popular Pharmaceutical Aluminum Foil Blister Packaging Materials from HC Aluminum
| Aluminum Foil Type | Thickness Range |
| Ultra-Lightweight Aluminum Foil | 0.006 - 0.007 mm |
| Lightweight Aluminum Foil | 0.008 - 0.012 mm |
| Aluminum Strip Packaging Foil | 0.02 - 0.05 mm |
| Aluminum Blister Lid Foil | 0.012 - 0.025 mm |
| Aluminum Cold-Forming Foil | 0.045 - 0.06 mm |
Selection of Aluminum Blister Packaging for Different Applications
Application Scenarios and Packaging Choices in the Pharmaceutical Sector
The pharmaceutical industry is the largest market for aluminum blister packaging. Different types of medications require different packaging:
Oral Solid Dosage Forms
Suitable Packaging: Both ALU/plastic and ALU/ALU blisters are widely used.
Common Thickness:
ALU/plastic blisters: aluminum foil thickness 20–30μm, PVC rigid film thickness 250–300μm.
ALU/ALU blisters: total aluminum foil thickness 45–60μm, typically OPA/AL/PVC structure.
Selection Criteria:
Ordinary tablets, capsules: choose ALU/plastic blisters, which are lower cost and easier to open.
Moisture-sensitive drugs: use ALU/ALU blisters for higher barrier protection.
Drugs requiring long-term storage: prioritize ALU/ALU blisters to extend shelf life.
Drugs to be sold in hot and humid regions: select ALU/ALU blisters for harsh environment adaptability.
Inhalation Dosage Forms
Suitable Packaging: ALU/ALU blisters.
Common Thickness: total aluminum foil thickness 50–60μm, typically PA/AL/PE structure.
Selection Criteria: inhalation products require excellent barrier performance, and ALU/ALU blisters provide complete protection against moisture and oxidation.
Application Scenarios and Packaging Choices in the Food Sector
The food sector is the second largest application market for aluminum blister packaging. Different food types require different packaging solutions:
Snack Foods
Suitable Packaging: ALU/plastic blisters and aluminum-paper/PET composite blisters.
ALU/plastic blisters: aluminum foil thickness 20–30μm, plastic rigid film thickness 200–300μm, commonly using PP or PET materials.
Aluminum-paper/PET composite blisters: aluminum foil thickness 20–30μm, paper or PET layer thickness 30–50μm.
Nuts, chocolates, and other oxidation-sensitive foods: choose ALU/plastic blisters for excellent moisture and oxygen barrier.
Premium products like gum or coffee capsules: aluminum-paper/PET composite blisters enhance product grade.
Foods requiring product display: use ALU/plastic blisters with transparent plastic film for visibility.
Ready-to-Eat Foods and Prepared Dishes
Suitable Packaging: ALU/plastic blisters, typically using high-temperature-resistant materials.
Common Thickness: aluminum foil thickness 30–40μm, plastic rigid film thickness 300–500μm, typically heat-resistant PP or PET.
High-temperature sterilized ready-to-eat meals: choose heat-resistant ALU/plastic blisters that withstand 121°C sterilization.
Foods requiring microwave heating: choose microwaveable ALU/plastic blisters, usually made of special plastic formulations.
Ready-to-eat meals requiring extended shelf life: use high-barrier ALU/plastic blisters to reduce oxygen transmission rate.
Aluminum blister foil is suitable for hard packaging of medical and pharmaceutical products such as pills, capsules, and tablets. The thickness of the aluminum foil typically ranges from 25 to 28 microns. The shiny side is coated with a heat-seal coating, while the matte side is treated with a printed coating.
Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pills and Capsules: Aluminum blister foil is commonly used for the unit packaging of pills and capsules, providing good sealing and moisture barrier properties to ensure the stability and efficacy of the medications. Each blister unit can hold one pill or one capsule, facilitating dose control.
Tablets: For various types of tablets, aluminum blister foil effectively prevents oxidation, moisture, and light exposure, ensuring the shelf life of the drugs, especially for those sensitive to environmental factors.
Multi-Dose Packaging for Pharmaceutical Products
Blister Packaging: Suitable for medications with multiple doses, typically designed with several blister units in the packaging, allowing patients to take doses as needed. This also reduces the risk of drug exposure, maintaining the quality of the medications.
Unit Design: A well-designed blister layout separates each dose, reducing the risk of cross-contamination and making it easier for patients to identify and use the medication.
The application of aluminum blister foil spans various fields, including pharmaceuticals, health supplements, and clinical trials. Its excellent protective properties, sealing capability, and print adaptability make it the preferred material for pharmaceutical packaging.
Aluminum Blister Packaging Production Process
ALU/ALU Blister Packaging Production Process
The production process of ALU/ALU blister packaging mainly includes the following key steps:
Raw Material Preparation
Aluminum foil: Usually soft-temper aluminum foil of alloy 8011, 8021, or 8079 is selected, with a thickness of 45–60μm. The surface is required to be clean and free of oil stains.
Polyamide (OPA) film: Thickness of 15–25μm, required to have excellent ductility and mechanical strength.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) film: Thickness of 60–100μm, used as the heat-sealing layer, and must possess good heat-sealing performance.
Adhesive: Special adhesive is selected to withstand the strong impact of forming without delamination or cracking, and must also be resistant to aging.
Laminating Process
There are two main laminating processes for ALU/ALU blister packaging:
One-step lamination: The three-layer materials—polyamide, aluminum foil, and PVC—are laminated into an integrated structure in a Class D cleanroom in a single process.
Process flow: Raw material preparation → Lamination → Curing → Slitting → Inner packaging → Outer packaging.
Step-by-step lamination: Some layers are laminated first, followed by curing, and then laminated with the remaining materials.
Process flow: Raw material preparation → First lamination → Curing → Second lamination → Curing → Slitting → Inner packaging → Outer packaging.
ALU/Plastic Blister Packaging Production Process
The production process of ALU/plastic blister packaging differs from that of ALU/ALU blister packaging and mainly includes the following steps:
Aluminum foil: Usually alloy 8011-H18 aluminum foil with a thickness of 20–30μm, required to have a clean and flat surface.
Plastic rigid film: Common materials include PVC, PP, or PET, with a thickness of 150–300μm.
Inks and coatings: Used for printing and coating on the surface of the aluminum foil.
Aluminum Foil Treatment
Surface treatment: The aluminum foil surface is treated through chemical or physical methods to improve adhesion of ink and coatings.
Printing: Gravure printing technology is used to print text and graphics on the aluminum foil surface.
Coating: A protective layer and heat-sealing layer are coated on the aluminum foil surface to protect the printed patterns and provide good heat-sealing performance.
Aluminum and Paper/PET Composite Blister Packaging Production Process
The production process of aluminum and paper/PET composite blister packaging involves the combination of aluminum foil, paper or PET film, and a heat-sealing layer. It mainly includes the following steps:
- Aluminum foil: Thickness of 20–30μm, required to be clean and free of pinholes.
- Paper or PET film: Thickness of 30–50μm, required to have a flat surface and high strength.
- Heat-sealing layer material: Usually a specially formulated hot melt adhesive or polymer material.
- Adhesive: Used for bonding between each material layer.
Advantages of Aluminum Blister Packaging
- Excellent Barrier Protection: Effectively blocks moisture, oxygen, and light.
- Extended Shelf Life: Maintains drug stability and efficacy over time.
- Tamper Evidence: Provides secure sealing, indicating any unauthorized access.
- Child-Safe Options: Can be designed to prevent accidental ingestion by children.
- Eco-Friendly: Aluminum is recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Dose Control: Individual compartments help prevent overdose.
- Child Safety: Requires pressing or tearing to open.
- Customization: Allows for branding, dosage information, or NFC tag printing.
- Protective: Shock- and pressure-resistant, reduces damage during transport
- Convenience: Individually packaged for easy access, supports customization such as braille printing
Limitations of Aluminum Blister Packaging
- Higher Production Cost: More expensive materials and manufacturing processes compared to standard blister packaging.
- Opacity: The non-transparent nature of aluminum makes it impossible to visually inspect the product without opening.
- Larger Package Size: Aluminum blister packaging tends to be bulkier, potentially affecting storage and transportation efficiency.
HC Aluminum Blister Packaging Product Quality Control System
As a professional supplier of raw materials for aluminum blister packaging, HC Aluminum has established a rigorous and comprehensive quality control system to ensure that each batch of raw materials meets high-standard requirements from the source.
In terms of aluminum foil quality control:
Thickness inspection: High-precision thickness gauges are used to check the thickness of aluminum foil, ensuring compliance with tolerance standards.
Pinholes inspection: Pinholes on aluminum foil are inspected using a pinhole inspection table to ensure no more than one pinhole of 0.1–0.3mm diameter per square meter.
Surface quality inspection: The aluminum foil surface is checked for scratches, dents, oil stains, and other defects.
For plastic material quality control:
Physical property testing: Testing the plastic material’s tensile strength, elongation at break, and other mechanical properties.
Thermal property testing: Testing the plastic material’s melting point, heat deformation temperature, and other thermal properties.
Barrier property testing: Testing the water vapor transmission rate and oxygen transmission rate of the plastic materials.
Hygiene testing: For pharmaceutical and food packaging, hygiene performance of the plastic materials must be tested to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
HC Aluminum firmly believes that only through strict quality control at every stage can we provide customers with reliable raw materials and achieve long-term win-win cooperation. We will continue to invest resources and optimize our quality control system to meet higher standards and stricter requirements, fulfilling our responsibility and commitment as a premium supplier.
Why is Blister Packaging So Popular for Pharmaceuticals?
Below is a summary of reasons why blister packaging is popular for pharmaceuticals, presented in a table format:
| Reason | Detailed Explanation |
| Product Integrity | Medications are sensitive to moisture, oxygen, and light. By selecting suitable blister packaging materials (such as lid foil), an effective barrier can be formed to prevent drug degradation. |
| Protection | Physical damage to the lid is required to access the medication, making it easy to identify potential product or packaging tampering. Additionally, it meets child safety standards, reducing the risk of child poisoning. |
| Customization | The blister packaging tray cavities can be customized, allowing tablets to be securely nested to prevent crushing and damage during transport or handling. |
| Dose Compliance | Each blister unit contains a single dose, making it easy for patients to track medication dosage and accuracy. Pre-printed daily or weekly reminders help patients maintain their medication routine. |
Related Questions
| Question/Information | Detailed Explanation |
| Difference Between Alu Alu and Blister Packaging | Material Composition: Blister packaging typically consists of a plastic base (PVC or PVDC) and an aluminum foil layer; Alu Alu packaging is made from two layers of heat-sealed aluminum foil. |
| Barrier Performance: Alu Alu offers superior barrier performance. | |
| Cost and Production: Alu Alu has a higher production cost. | |
| Thickness of Aluminum Foil for Blister Packaging | Typically ranges from 20 to 30 microns (0.02 to 0.03 mm). |
| Uses of Aluminum Blister Foil | Pharmaceutical Packaging: Used for packaging tablets and capsules, protecting drugs from moisture, oxygen, and light exposure. |
| Nutritional Supplements: Used for packaging vitamins and dietary supplements. | |
| Food Products: Packaging for certain sensitive food items. | |
| Clinical Trials: Used for compliant packaging of pharmaceuticals. |