PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Packaging
PVC/PVDC aluminum blister is a high-performance composite structure widely used in pharmaceutical packaging. Its core is composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) composite rigid film, with an aluminum foil sealing layer on the surface.
PVC/PVDC aluminum blister packaging is a protective solution extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry for solid oral medications such as tablets and capsules. This packaging combines multiple materials to provide optimal environmental protection, ensuring drug efficacy and shelf life.
PVC/PVDC aluminum blister packaging provides a reliable and effective method to protect medications, ensuring their safety, effectiveness, and durability.
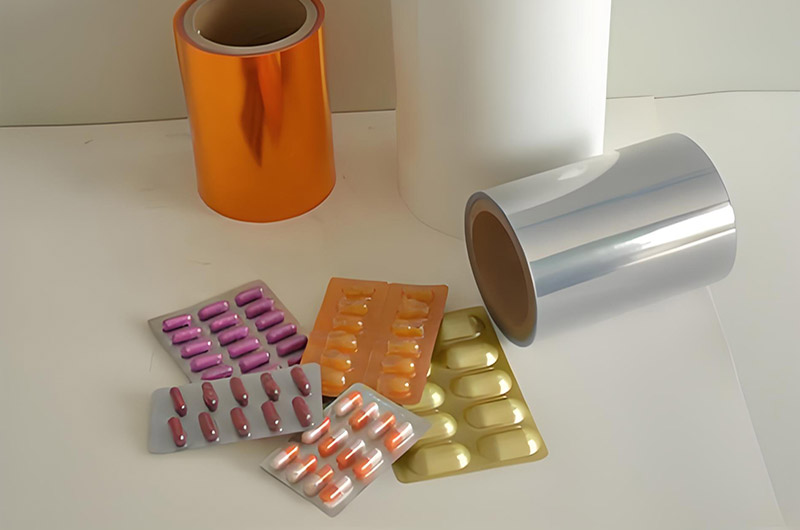

PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), PVDC (Polyvinylidene Chloride), and aluminum are key pharmaceutical packaging materials that protect drugs from oxygen, odors, moisture, water vapor penetration, contamination, and bacteria. To meet increasing packaging demands, the three materials are often used in combination to leverage their respective advantages.
PVC-coated PVDC films are available in various specifications and are suitable for blister packaging in the pharmaceutical and food industries. They are sealed with aluminum blister foil, which is the most commonly used material for blister forming.
PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Composition and Structure
A typical PVC/PVDC aluminum blister package contains the following layers:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Serves as the base material, providing structural integrity and formability. The typical thickness range of PVC is 200–300 microns (0.20–0.30 mm), with 250 microns being the most commonly used thickness for pharmaceutical applications.
- PVDC (Polyvinylidene Chloride): Coated on the PVC layer to enhance barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and other gases. PVDC coating weights vary (e.g., 40/60/90/120 gsm), with higher weights offering superior protection against moisture, oxygen, and odors.
- Aluminum Foil: Used as the lidding material, providing additional protection against light, moisture, and contamination. It is sealed onto the PVC/PVDC film to form a sealed compartment. The aluminum foil acts as a secondary barrier and allows tablets or capsules to be easily pushed through.
This multilayer structure ensures that the medication is well protected from external factors that may affect its quality.
- Composite Method: Typically employs coating, lamination, and other processes to tightly bond the three-layer materials, forming a complete composite film.
- Heat Sealing Technology: Forms good heat sealing properties with PVC, creating a blister-sealed chamber in combination with aluminum foil.
- Application Fields: Widely used for packaging moisture- or oxygen-sensitive drugs such as antibiotics, vitamins, anti-allergy medicines, and contraceptives.
PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Specifications
| Item | Specifications and Descriptions |
| Thickness | PVC Thickness: 0.20–0.45 mm (typically 250µ or 300µ) |
| Special Applications: Customizable thickness up to 1000 µm | |
| Moisture Barrier (WVTR) | The thicker the PVDC coating, the lower the water vapor transmission rate |
| 40 gsm PVDC: ≤ 0.8 g/m²/24h | |
| 120 gsm PVDC: ≤ 0.4 g/m²/24h | |
| Oxygen Barrier (OTR) | Oxygen transmission rate of high-coated PVDC film can be as low as 0.1 cc/m²/day |
| Color and Customization | Available in transparent, white, silver, or opaque colors (e.g., yellow, orange, etc.) |
| UV filters or pigments can be added upon request |
PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Features
- Enhanced Barrier Protection: PVDC coating significantly improves moisture and gas resistance, making it suitable for sensitive drugs requiring strict protection.
- Transparency: The transparent nature of PVC allows for visual inspection of the drug, helping to identify and reduce the risk of errors.
- Mechanical Strength: PVC provides the necessary rigidity and strength to withstand the pressure during handling and transportation without compromising the integrity of the blister.
- Chemical Resistance: The combination of PVC and PVDC can withstand various chemicals, ensuring the packaging does not adversely react with the medication.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared with other high-barrier materials, PVC/PVDC strikes a balance between performance and cost, making it a preferred choice for many pharmaceutical applications.
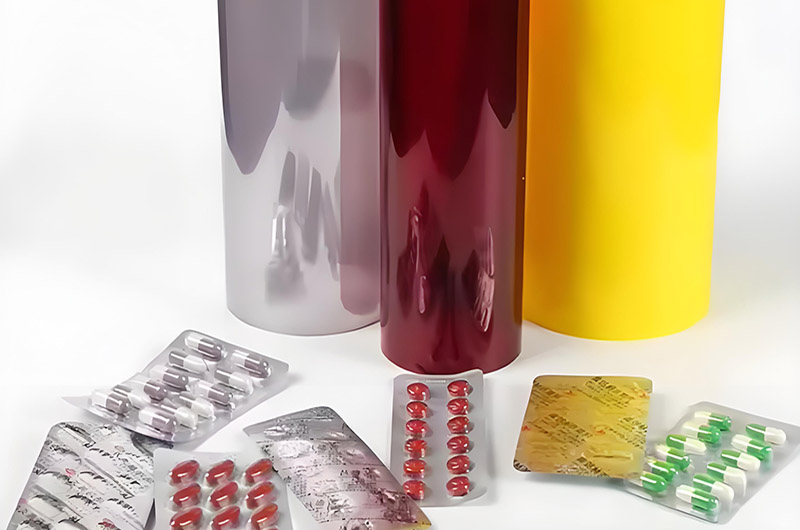

PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Applications
PVC/PVDC aluminum blister packaging is mainly used for:
- Solid oral dosage forms: such as tablets and capsules, especially suitable for formulations sensitive to moisture and oxygen.
- Unit dose packaging: helps in accurate dosing and improves patient compliance.
- Tablets, capsules, and hygroscopic or photosensitive medications.
- Suppositories and liquid medications (via PVC/PE composite materials).
- Food-grade packaging produced according to pharmaceutical-grade standards (e.g., candies, chewing gum).
- Shelf-life extension products: medications that need to remain stable under various environmental conditions for a long period.
PVC/PVDC blister packaging offers excellent protection performance, but due to the material combination, recycling may pose challenges.
PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Advantages
- Enhanced Protection: Combines the rigidity of PVC with the high barrier properties of PVDC to effectively block moisture, oxygen, and contaminants.
- Cost Effectiveness: Lower production costs compared to alternatives such as PCTFE or COC laminated sheets.
- Thermoforming Efficiency: Compatible with rotary and flat blister machines for high-speed production.
Performance of PVC PVDC ALU Blister Materials
| Performance Indicator | PVC Blister | PVDC Blister | ALU Blister |
| Barrier Properties | Medium, some barrier against water, oxygen, and odors, but limited | Excellent, extremely high barrier to water, oxygen, odors, and chemicals | Outstanding, completely blocks light, oxygen, moisture, and odors |
| Transparency | Good, high product visibility | Good, high product visibility | Opaque, fully blocks light |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium, certain impact and abrasion resistance | Good, high tensile strength and flexibility | Medium, lower tensile strength but higher hardness |
| Processability | Good, easy for thermoforming and heat sealing | Medium, more difficult to process than PVC | Medium, requires special forming process |
| Temperature Resistance | Poor, may release harmful substances at high temperatures | Good, usable across a wide temperature range | Excellent, suitable for extreme temperature conditions |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, certain resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent, highly resistant to various chemicals | Good, surface forms a protective oxide layer |
| Moisture Resistance | Medium, limited moisture protection when used alone | Excellent, extremely strong barrier to water vapor | Excellent, completely moisture-proof |
| Cost | Low, the lowest among the three materials | Medium-high, higher than PVC but lower than ALU | High, especially for Alu-Alu structures |
| Environmental Performance | Poor, difficult to recycle, may emit harmful substances when burned | Poor, hard to recycle, improper handling may pollute the environment | Good, fully recyclable, high recycling value |
| Typical Thickness | 0.1–0.5 mm, commonly 0.25 mm | 0.09–1.00 mm, commonly 0.25 mm base + 40–120 g/m² coating | 0.01–0.1 mm, commonly 20–30 μm (pharmaceutical) or 45–60 μm (cold forming) |
PVC PVDC ALU Blister Material Combinations
To meet increasing packaging demands, the three materials are often combined to leverage their respective advantages:
PVC/PVDC Composite
PVC base provides basic structure and formability, while the PVDC coating offers excellent barrier performance.
Common specification: 250µ PVC base + 40–120 g/m² PVDC coating, widely used in pharmaceutical and food packaging.
Recent developments show that triple-layer structures (PVC/PE/PVDC) now account for 18% of PVDC film sales due to excellent deep-draw forming performance for complex blister geometries.
Alu/PVC Composite
PVC base provides flexibility and formability, while aluminum foil lid offers superior barrier properties.
Alu-PVC blister is a cost-effective packaging solution with sufficient protective performance.
Lower cost than Alu-Alu blister, but slightly inferior in protection.
Alu/PVDC Composite
Combines aluminum foil’s full light blocking with PVDC’s high gas barrier properties.
Provides extremely high barrier performance, suitable for products highly sensitive to light, moisture, and oxygen.
High cost, used only for high-end or special-demand products.
Comparison of PVC PVDC ALU Blister Materials
Environmental Performance Comparison
PVC Environmental Performance
Difficult to recycle, requires special processes
Poor biodegradability in the natural environment
Production may generate harmful by-products
Releases toxic gases when burned
PVDC Environmental Performance
Extremely difficult to recycle, technology underdeveloped
Also difficult to degrade
Production and disposal may release harmful substances
Significant environmental impact
ALU Environmental Performance
High recycling value
Mature recycling technology, high recycling rate
High production energy consumption, but recycling requires only 5% of original aluminum’s energy
Aligned with circular economy principles
Applications
Pharmaceutical Industry
General medicines: PVC blister
High-value medicines: PVDC-coated PVC or Alu-Alu
Highly sensitive medicines: Alu-Alu cold-formed blister
Food Industry
Fresh fruits and vegetables: PVC blister
Meat, cheese: PVDC-coated films
Premium foods: ALU blister
Electronics Industry
General electronics: PVC blister
Precision components: ALU blister
Sensitive components: PVDC or Alu-PVC composite blister
PVC Blister
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Blister
A thermoplastic packaging material made primarily from polyvinyl chloride resin, with appropriate amounts of anti-aging agents, modifiers, etc., produced through mixing, calendaring, vacuum forming, and other processes.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
PVC material features light weight, heat insulation, thermal preservation, moisture resistance, flame retardancy, and ease of processing. It comes in various specifications, rich colors, and patterns with strong decorative qualities. It is one of the most widely used decorative plastic materials and plays an important role in the packaging field.
Application Scenarios and Industry Uses
With its unique advantages, PVC blister is widely used in multiple industries:
- Pharmaceutical industry: used for packaging solid oral preparations such as tablets and capsules, offering transparency, durability, and tamper resistance
- Food industry: used in packaging fresh fruits and vegetables, baked goods, and ready-to-eat foods to extend shelf life
- Electronics industry: used for packaging small electronic products, components, and accessories, offering insulation and mechanical strength
- Consumer goods industry: used in cosmetics, daily necessities, and small consumer goods packaging, benefiting from its transparency and custom design capability
Common Specifications and Sizes
PVC blister comes in a variety of specifications depending on application needs:
Thickness: typically ranges from 0.1–0.5 mm; 200–300 microns commonly used in pharmaceutical packaging
Width: roll widths vary widely, with standard widths such as 100 mm, 200 mm, and 500 mm
Forming size: can be shaped into cavities of various shapes and sizes to suit different packaging needs
Core size: usually uses 76 mm (3-inch) paper or plastic cores
Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical Properties
Transparency: good clarity and gloss
Mechanical strength: certain mechanical strength with good impact and abrasion resistance
Formability: easy to thermoform, suitable for customized packaging needs
Heat sealability: good heat sealing performance, can form a reliable seal with lid materials such as aluminum foil
Hardness: appropriate hardness to maintain package shape stability
Chemical Properties
Chemical resistance: good chemical stability with resistance to acids, alkalis, etc.
Barrier performance: low permeability to oils, fats, and flavoring agents
Moisture resistance: certain moisture protection, though limited when used alone
Temperature resistance: relatively poor heat resistance; may release harmful substances at high temperatures
Weather resistance: good resistance to weathering and not prone to fading
Comparison with Similar Materials
Compared with other commonly used blister materials, PVC has the following characteristics:
Compared with PP: PVC has higher density, better transparency, and easier thermoforming, but inferior environmental performance
Compared with PETG: PETG is softer than PET, has lower density, and better temperature resistance
Compared with PVDC: PVDC has superior barrier properties but is more expensive and harder to process
PVDC Blister
PVDC (Polyvinylidene Chloride) Blister
A polymer material polymerized mainly from vinylidene chloride monomers, usually used in the form of films or coatings, with excellent barrier properties.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
PVDC material has excellent barrier properties and extremely high resistance to moisture, oxygen, and chemical substances, making it an ideal choice for high-demand packaging applications.
Application Scenarios and Industry Uses
Due to its superior barrier properties, PVDC blister material is widely used in several key industries:
- Food industry: used in the packaging of meat, cheese, baked goods, snack foods, and other ready-to-eat products to maintain product freshness
- Pharmaceutical industry: used for packaging moisture- and oxygen-sensitive medications, protecting solid oral drug formulations
- Consumer goods industry: used for high-end cosmetics, personal care products, and precision electronics packaging
- Industrial applications: used in packaging for certain industrial products, especially those sensitive to chemicals
Common Specifications and Sizes
The specifications and sizes of PVDC blister material vary depending on application requirements:
Thickness: Pure PVDC sheet thickness is usually between 0.09–1.00 mm; common coating weights include 40 g/m² and 60 g/m²
Width: Slit roll widths usually range from 70–300 mm; jumbo roll widths generally range from 500–1500 mm
Core size: Typically 76 mm inner diameter; available with paper or plastic cores
Physical specs: Density approximately 1.7–1.8 g/cm³; high tensile strength
Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical Properties
Barrier properties: Excellent gas barrier properties, providing extremely high resistance to oxygen, water vapor, and odors
Moisture resistance: Extremely strong water vapor barrier, effectively prevents product moisture absorption
Mechanical properties: Good tensile strength and flexibility
Heat sealability: Good heat seal performance, forms reliable seals with various materials
Transparency: Good transparency, allowing visibility of the packaged product
Chemical Properties
Chemical resistance: Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and organic solvents
Temperature resistance: Good thermal stability across a wide temperature range
Flame resistance: Self-extinguishing, not easily flammable
Stability: Chemically stable under normal storage conditions
Comparison with Similar Materials
Compared to other high-performance blister materials, PVDC has the following characteristics:
Compared to EVOH: PVDC’s barrier properties are not affected by humidity; it has better chemical resistance but inferior processability
Compared to PVC: PVDC offers significantly better barrier properties but is harder to process and more expensive
Compared to aluminum foil: Aluminum foil provides superior barrier properties, especially against light, but PVDC is more flexible
ALU (Aluminum Foil) Blister
ALU (Aluminum Foil) Blister
A metal foil blister material made from aluminum via rolling and other processes, offering extremely high barrier performance and completely blocking light, oxygen, and moisture.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
Aluminum foil blister materials have excellent barrier performance, completely blocking light, oxygen, and moisture to provide superior protection for sensitive products.
Application Scenarios and Industry Uses
ALU blister materials, thanks to their unique barrier and physical properties, are widely used in several high-end industries:
- Pharmaceutical industry: Used for high-value medicines sensitive to humidity, oxygen, and light, such as Alu-Alu cold-formed blister packs
- Food industry: Applied in high-end food and health products, such as chocolate, tea, coffee, and specialty nutritional products
- Electronics industry: Used for packaging electronic components and precision instruments sensitive to static and electromagnetic interference
- Luxury goods industry: Used in high-end cosmetics, perfumes, and luxury products to enhance brand image
Common Specifications and Sizes
ALU blister materials come in various specifications depending on application needs:
Thickness: Pharmaceutical-grade aluminum foil is typically 20–30 microns thick; cold-formed aluminum foil is usually 45–60 microns
Width: Standard widths typically range from 300–1100 mm; custom widths are available
Core size: Commonly 76 mm or 152 mm inner diameter, with options for steel or aluminum cores
Physical specs: Common alloy is 8011; tensile strength typically ≥180 MPa
Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical Properties
Barrier properties: Excellent barrier performance, completely blocks light, oxygen, moisture, and odors
Thermal conductivity: Good thermal conductivity, fast heat transfer
Light-blocking: Fully opaque, 100% light barrier
Flexibility: Certain flexibility, suitable for both thermoforming and cold-forming processes
Metallic luster: Metallic shine enhances the visual appeal of packaging
Chemical Properties
Corrosion resistance: An aluminum oxide film easily forms on the surface, providing good corrosion resistance
Stability: Chemically stable under normal storage conditions
Temperature resistance: Good temperature resistance, usable across a wide temperature range
Comparison with Similar Materials
Compared to other high-performance blister materials, ALU has the following characteristics:
Compared to VMPET: Aluminum foil offers superior barrier properties but has higher cost and poorer processability
Compared to PVC: Significantly better barrier properties but higher cost and lower tear resistance
Compared to PVDC: Better light barrier properties but lower flexibility and puncture resistance
Key Factors in Selecting PVC, PVDC, and ALU Blister Materials
- Product characteristics: shape, size, weight, hardness, pH level, sensitivity, etc.
- Packaging requirements: barrier properties, mechanical performance, appearance, processability, etc.
- Cost factors: material cost, transportation cost, storage cost, overall cost-effectiveness
- Environmental requirements: recyclability, degradability, environmental impact, carbon footprint
- Market demand: target market expectations, product positioning, brand image, consumer acceptance
Comprehensive Recommendations for PVC, PVDC, and ALU Blisters
Pharmaceutical Packaging Recommendations
Regular solid oral dosage forms: PVC blisters or Alu-PVC blisters
High-value or sensitive drugs: PVC/PVDC composite blisters or Alu-Alu blisters
Highly sensitive medications: Alu-Alu cold-formed blisters
Food Packaging Recommendations
Fresh fruits, vegetables, and daily products: PVC blisters
Meat, seafood, and moist foods: PVDC-coated films
Premium chocolate, tea, and coffee: ALU blisters
Environmental Packaging Recommendations
Projects with high environmental requirements: prioritize ALU blisters
Projects with moderate environmental requirements: recyclable PVC or PVDC blisters
To reduce environmental impact of packaging: optimize packaging design and use lightweight materials
PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Production Process Flow
| Process Step | Description |
| Rigid Film Pre-treatment | PVC/PVDC rigid film is softened using a heating device. |
| Heating temperature is controlled at 120–150℃ to improve plasticity and facilitate forming. | |
| Blister Forming | Uses vacuum forming or pressure forming processes. |
| Forming blister cavities on the mold. | |
| Forming depth: Standard for pharmaceutical packaging is 3–10mm; special applications (e.g. medical devices) up to 60mm. | |
| Drug Filling and Lamination | After cooling the blister, drugs are filled. |
| Aluminum foil is applied and sealed using a heat sealing device. | |
| Sealing temperature is 160℃ ± 5℃; pressure sealing ensures sealing strength ≥ 1.5N/15mm. | |
| Post-treatment | Includes printing, punching, and final product inspection. |
| Inspection items include: heat seal strength, barrier performance tests, etc., to ensure product quality. |
PVC/PVDC Aluminium Blister Key Performance Indicators
| Performance Category | Indicator Item | Specific Requirements and Description |
| Mechanical Properties | Tensile Strength | Average value (longitudinal/transverse) ≥ 40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Passed drop ball impact test (steel ball free fall), number of damaged samples in both directions ≤ 2 | |
| Thermal Properties | Heat Seal Strength | Ensures sealing integrity; heat seal test values must meet requirements of standards such as the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. |
| Thermal Shrinkage Rate | Dimensional changes after heating must be within ±6%. | |
| Barrier Properties | Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR) | PVDC composite layer can reduce oxygen transmission rate to ≤ 5 cm³/(m²·24h·0.1MPa) |
| Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR) | Aluminum foil composite structure achieves WVTR ≤ 0.1 g/(m²·24h), providing excellent moisture resistance. |